It sure has changed my workflow.
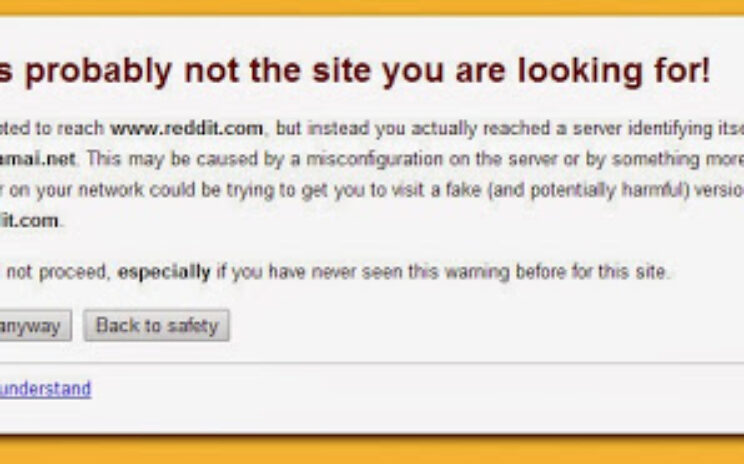
Hmmm…? www.reddit.com – I think your SSL cert does not like you.. View this post on Google+
Hmmm…? www.reddit.com – I think your SSL cert does not like you..
This is exactly how long it takes a train to pass when you need to be anywhere that's not sitting at the only train crossing that is never used all year till you pull up to it… This post has been reshared 1 times on Google+ View this post on Google+
This is exactly how long it takes a train to pass when you need to be anywhere that's not sitting at the only train crossing that is never used all year till you pull up to it…
Especially for free… Agent – do not disturb & more Agent is a must have app for any Android user and gives you these essential… View this post on Google+
Now this is an interesting app for android….. Especially for free… Agent – do not disturb & moreAgent is a must have app for any Android user and gives you these essential…
Reshared post from +NASA As seen on #Cosmos: Supernova A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space. Supernovas are often seen in other galaxies. But supernovas are difficult to see in our own Milky Way galaxy because dust blocks our view. In 1604, Johannes Kepler discovered the last observed supernova in the Milky Way. NASA’s Chandra telescope discovered the remains of a more recent supernova. It exploded in the Milky Way more than a hundred years ago. A supernova happens where there is a change in the core, or center, of a star. A change can occur in two different ways, with both resulting in a supernova. The first type of supernova happens in binary star systems. Binary stars are two stars that orbit the same point. One of the stars, a carbon-oxygen white dwarf, steals matter from its companion star. Eventually, the white dwarf accumulates too much matter. Having too much matter causes the star to explode, resulting in a supernova. The second type of supernova occurs at the end of a single star’s lifetime. As the star runs out of nuclear fuel, some of its mass flows into […]
This is what my neck feels like tonight…. Originally shared by +NASA As seen on #Cosmos: Supernova A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space. Supernovas are often seen in other galaxies. But supernovas are difficult to see in our own Milky Way galaxy because dust blocks our view. In 1604, Johannes Kepler discovered the last observed supernova in the Milky Way. NASA’s Chandra telescope discovered the remains of a more recent supernova. It exploded in the Milky Way more than a hundred years ago. A supernova happens where there is a change in the core, or center, of a star. A change can occur in two different ways, with both resulting in a supernova. The first type of supernova happens in binary star systems. Binary stars are two stars that orbit the same point. One of the stars, a carbon-oxygen white dwarf, steals matter from its companion star. Eventually, the white dwarf accumulates too much matter. Having too much matter causes the star to explode, resulting in a supernova. The second type of supernova occurs at the end of a single star’s lifetime. As the star runs out of […]
Imagine being able to watch as Edison turned on the first light bulb, or as Franklin received his first jolt of electricity. For the first time, a film gives audiences a front row seat to a significant and inspiring scientific breakthrough as it happens. Particle Fever follows six brilliant scientists during the launch of the Large Hadron Collider, marking the start-up of the biggest and most expensive experiment in the history of the planet, pushing the edge of human innovation. As they seek to unravel the mysteries of the universe, 10,000 scientists from over 100 countries joined forces in pursuit of a single goal: to recreate conditions that existed just moments after the Big Bang and find the Higgs boson, potentially explaining the origin of all matter. But our heroes confront an even bigger challenge: have we reached our limit in understanding why we exist? Directed by Mark Levinson, a physicist turned filmmaker, and masterfully edited by Walter Murch (Apocalypse Now, The English Patient), Particle Fever is a celebration of discovery, revealing the very human stories behind this epic machine. View this post on Google+
Imagine being able to watch as Edison turned on the first light bulb, or as Franklin received his first jolt of electricity. For the first time, a film gives audiences a front row seat to a significant and inspiring scientific breakthrough as it happens. Particle Fever follows six brilliant scientists during the launch of the Large Hadron Collider, marking the start-up of the biggest and most expensive experiment in the history of the planet, pushing the edge of human innovation. As they seek to unravel the mysteries of the universe, 10,000 scientists from over 100 countries joined forces in pursuit of a single goal: to recreate conditions that existed just moments after the Big Bang and find the Higgs boson, potentially explaining the origin of all matter. But our heroes confront an even bigger challenge: have we reached our limit in understanding why we exist? Directed by Mark Levinson, a physicist turned filmmaker, and masterfully edited by Walter Murch (Apocalypse Now, The English Patient), Particle Fever is a celebration of discovery, revealing the very human stories behind this epic machine.
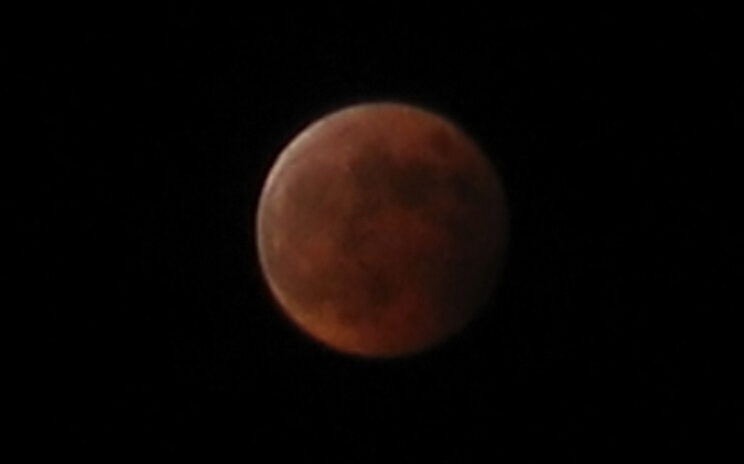
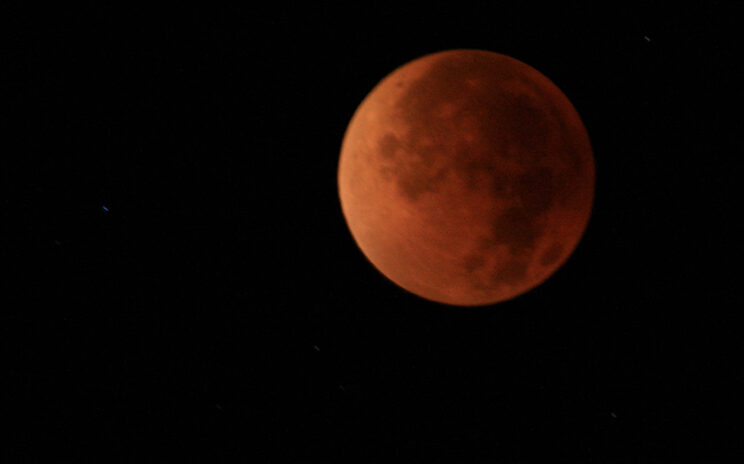
In album Astrophotography TOTAL LUNAR ECLIPSE: On Tuesday morning, April 15th, the full Moon will pass through the shadow of Earth, producing a colorful lunar eclipse. Although the mainstream media is calling this a "blood moon," the color is more likely to be bright orange. At the moment, Earth's stratosphere is not dusty enough produce a shadow with the deep red hues of blood. Whatever color it turns out to be, the eclipse will be visible from North and South America, Australia and New Zealand. Check http://spaceweather.com for observing tips and more information. LIVE WEBCAST OF THE ECLIPSE: Got clouds? No problem. The lunar eclipse will be broadcast live on the web by the Coca-Cola Science Center at Columbus State University in Georgia: http://www.ccssc.org/webcast.html Reshared post from +Jeff Sullivan Total Lunar Eclipse Tomorrow NightDepending upon where you live on the planet, a lunar eclipse will occur starting either late April 14 or in the early morning hours of April 15. NASA provides the times in Universal TIme (UT):http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/OH/OH2014.html#LE2014Apr15T For viewers in North America, here's the approximate timing for viewers on the West Coast (PDT time zone): 10:58pm (Mon) partial lunar eclipse begins12:07am (Tues) total lunar eclipse begins12:47am (Tues) maximum […]
TOTAL LUNAR ECLIPSE: On Tuesday morning, April 15th, the full Moon will pass through the shadow of Earth, producing a colorful lunar eclipse. Although the mainstream media is calling this a "blood moon," the color is more likely to be bright orange. At the moment, Earth's stratosphere is not dusty enough produce a shadow with the deep red hues of blood. Whatever color it turns out to be, the eclipse will be visible from North and South America, Australia and New Zealand. Check http://spaceweather.com for observing tips and more information. LIVE WEBCAST OF THE ECLIPSE: Got clouds? No problem. The lunar eclipse will be broadcast live on the web by the Coca-Cola Science Center at Columbus State University in Georgia: http://www.ccssc.org/webcast.html Originally shared by +Jeff Sullivan Total Lunar Eclipse Tomorrow NightDepending upon where you live on the planet, a lunar eclipse will occur starting either late April 14 or in the early morning hours of April 15. NASA provides the times in Universal TIme (UT):http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/OH/OH2014.html#LE2014Apr15T For viewers in North America, here's the approximate timing for viewers on the West Coast (PDT time zone): 10:58pm (Mon) partial lunar eclipse begins12:07am (Tues) total lunar eclipse begins12:47am (Tues) maximum lunar eclipse 1:25am (Tues) […]
Go read the mashable article with sites that were compromised Reshared post from +Robert Scoble Changing passwords is a pain in the behind. But everyone should be doing this because of the Heartbleed security problems that have come to surface the last few days: http://www.techmeme.com/140410/p3#a140410p3 Some things: 1. If you don't have a different password for each site you are doing it wrong! (Particularly for banks, email, and major social networks).2. If your password isn't at least 12 characters long, you are doing it wrong!3. If your passwords have ANY dictionary names in them, you are doing it wrong (things that appear in the dictionary).4. If you aren't using two-factor authentication on EVERY site that offers such (Gmail, Facebook, Twitter all do) then you are doing it wrong.5. If you aren't using a password manager like Lastpass then you are probably doing it wrong (I let it generate all my passwords now to make sure I get truly strong 20-character passwords). Good luck out there! The Heartbleed Hit List: The Passwords You Need to Change Right Now This story, by Mashable, appeared on Techmeme. This post has been reshared 4 times on Google+ View this post on Google+
Heartbleed SSL vulnerability… Go read the mashable article with sites that were compromised Originally shared by +Robert Scoble Changing passwords is a pain in the behind. But everyone should be doing this because of the Heartbleed security problems that have come to surface the last few days: http://www.techmeme.com/140410/p3#a140410p3 Some things: 1. If you don't have a different password for each site you are doing it wrong! (Particularly for banks, email, and major social networks).2. If your password isn't at least 12 characters long, you are doing it wrong!3. If your passwords have ANY dictionary names in them, you are doing it wrong (things that appear in the dictionary).4. If you aren't using two-factor authentication on EVERY site that offers such (Gmail, Facebook, Twitter all do) then you are doing it wrong.5. If you aren't using a password manager like Lastpass then you are probably doing it wrong (I let it generate all my passwords now to make sure I get truly strong 20-character passwords). Good luck out there! The Heartbleed Hit List: The Passwords You Need to Change Right NowThis story, by Mashable, appeared on Techmeme.
This post has been reshared 1 times on Google+ View this post on Google+
Nicely done mother nature..
Shtuff People Say to Photographers: http://youtu.be/niyTIbiV19A This post has been reshared 1 times on Google+ View this post on Google+
Shtuff People Say to Photographers: http://youtu.be/niyTIbiV19A
Rail gun tech makes me want to work at +BAE Systems, Inc.Hello Sci Fi here we come.. Advanced US Military Technology: Electromagnetic …: http://youtu.be/atwU5bgXEao This post has been reshared 1 times on Google+ View this post on Google+
Hello Sci Fi here we come.. Advanced US Military Technology: Electromagnetic …: http://youtu.be/atwU5bgXEao
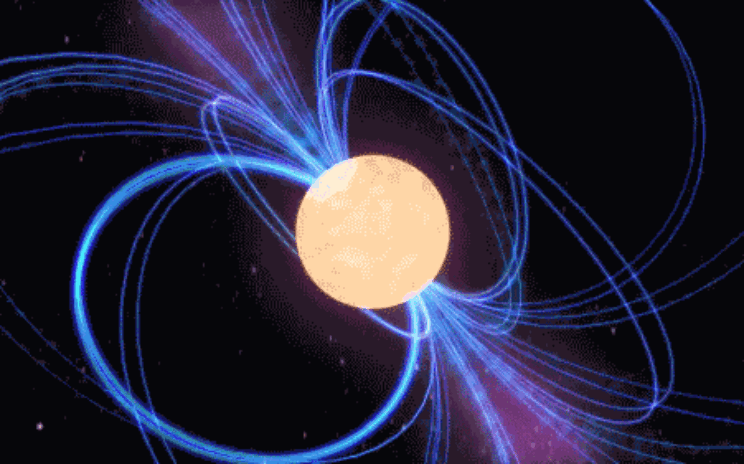
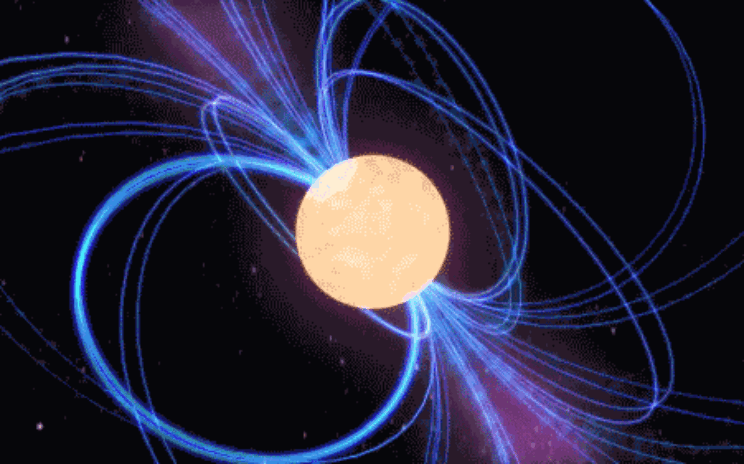
Reshared post from +annarita ruberto Pulsars, a kind of cosmic lighthouses The Pulsars (Pulsating Radio Sources) are rapidly rotating neutron stars with a very high magnetic field, which emit a collimated beam of radio waves.The radio emission, coming from the magnetic poles of the star, is confined within a small cone of emission and, if the magnetic axis is not aligned with the rotational one, the neutron star acts as a sort of cosmic lighthouse and an observer on Earth will see a sequence of pulses of radio waves. Let's see how a pulsar comes into being. When a massive star, exhausted its nuclear fuel, ends its life, it happens a supernova explosion and it remains a compact remnant . This object, named Neutron Star, has a radius of about 10 km and a mass equal about to 1.5 that one of the sun (whose radius is 700,000 miles). A Neutron Star is thus the "ash" that remains when a massive star collapses on itself and burns. The gravity force prevails on the electronic force that holds the atoms separated from each other and compresses them into a mass ten trillion times denser than a lead block. A single teaspoon […]
If I could I would want to see a neutron star before I die.. Originally shared by +annarita ruberto Pulsars, a kind of cosmic lighthouses The Pulsars (Pulsating Radio Sources) are rapidly rotating neutron stars with a very high magnetic field, which emit a collimated beam of radio waves.The radio emission, coming from the magnetic poles of the star, is confined within a small cone of emission and, if the magnetic axis is not aligned with the rotational one, the neutron star acts as a sort of cosmic lighthouse and an observer on Earth will see a sequence of pulses of radio waves. Let's see how a pulsar comes into being. When a massive star, exhausted its nuclear fuel, ends its life, it happens a supernova explosion and it remains a compact remnant . This object, named Neutron Star, has a radius of about 10 km and a mass equal about to 1.5 that one of the sun (whose radius is 700,000 miles). A Neutron Star is thus the "ash" that remains when a massive star collapses on itself and burns. The gravity force prevails on the electronic force that holds the atoms separated from each other and compresses them […]
to identity theives – thats awesome Fact-Checking Experian’s Talking Points — Krebs on Security In the wake of long-overdue media attention to revelations that a business unit of credit bureau Experian sold consumer personal data directly to an online service that catered to identity thieves, Experian is rightfully trying to explain its side of the story by releasing a series of talking … View this post on Google+
experian sells our personal data.. to identity theives – thats awesome Fact-Checking Experian’s Talking Points — Krebs on SecurityIn the wake of long-overdue media attention to revelations that a business unit of credit bureau Experian sold consumer personal data directly to an online service that catered to identity thieves, Experian is rightfully trying to explain its side of the story by releasing a series of talking …