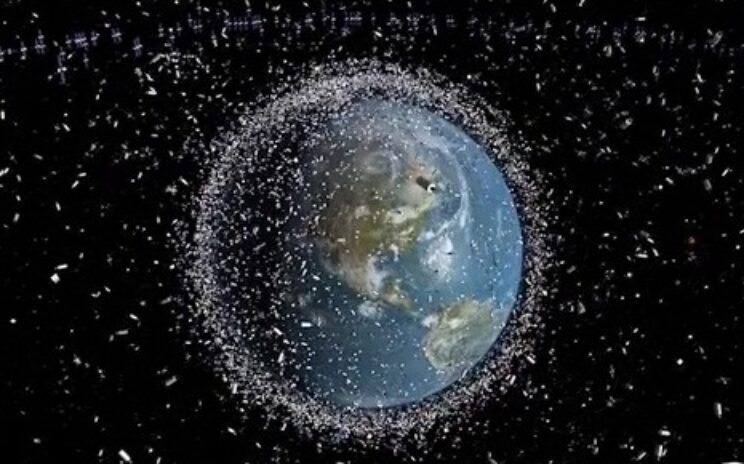
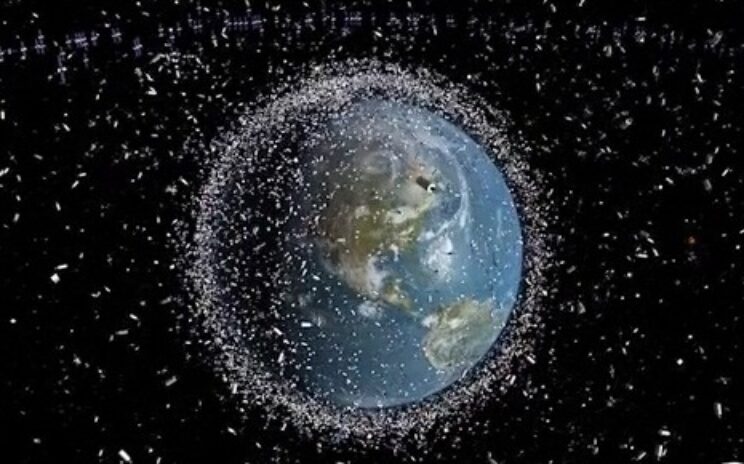
Reshared post from +Friends of NASA Space debris around Earth | European Space AgencyMore than half a century of launching into orbit has left Earth surrounded by a shroud of debris, formed of disused satellites and smaller fragments. Credit: European Space Agency (ESA)Released 28/05/2014 +European Space Agency, ESA #ESA #Space #Debris #Earth #Satellites #ISS #Orbit #Risk #Threat #International #Global #Humanity #Environment #SpaceDebris This post has been reshared 2 times on Google+ View this post on Google+
We clearly need to make a space Hoover….. Originally shared by +Friends of NASA Space debris around Earth | European Space AgencyMore than half a century of launching into orbit has left Earth surrounded by a shroud of debris, formed of disused satellites and smaller fragments. Credit: European Space Agency (ESA)Released 28/05/2014 +European Space Agency, ESA #ESA #Space #Debris #Earth #Satellites #ISS #Orbit #Risk #Threat #International #Global #Humanity #Environment #SpaceDebris
Reshared post from +NASA As seen on #Cosmos: Supernova A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space. Supernovas are often seen in other galaxies. But supernovas are difficult to see in our own Milky Way galaxy because dust blocks our view. In 1604, Johannes Kepler discovered the last observed supernova in the Milky Way. NASA’s Chandra telescope discovered the remains of a more recent supernova. It exploded in the Milky Way more than a hundred years ago. A supernova happens where there is a change in the core, or center, of a star. A change can occur in two different ways, with both resulting in a supernova. The first type of supernova happens in binary star systems. Binary stars are two stars that orbit the same point. One of the stars, a carbon-oxygen white dwarf, steals matter from its companion star. Eventually, the white dwarf accumulates too much matter. Having too much matter causes the star to explode, resulting in a supernova. The second type of supernova occurs at the end of a single star’s lifetime. As the star runs out of nuclear fuel, some of its mass flows into […]
This is what my neck feels like tonight…. Originally shared by +NASA As seen on #Cosmos: Supernova A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space. Supernovas are often seen in other galaxies. But supernovas are difficult to see in our own Milky Way galaxy because dust blocks our view. In 1604, Johannes Kepler discovered the last observed supernova in the Milky Way. NASA’s Chandra telescope discovered the remains of a more recent supernova. It exploded in the Milky Way more than a hundred years ago. A supernova happens where there is a change in the core, or center, of a star. A change can occur in two different ways, with both resulting in a supernova. The first type of supernova happens in binary star systems. Binary stars are two stars that orbit the same point. One of the stars, a carbon-oxygen white dwarf, steals matter from its companion star. Eventually, the white dwarf accumulates too much matter. Having too much matter causes the star to explode, resulting in a supernova. The second type of supernova occurs at the end of a single star’s lifetime. As the star runs out of […]
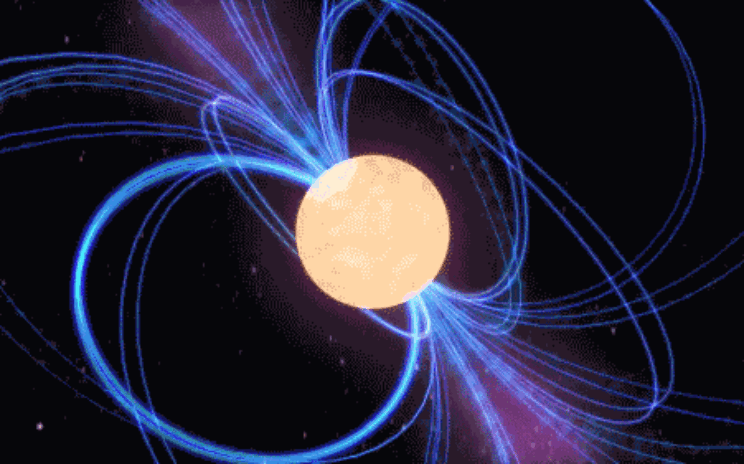
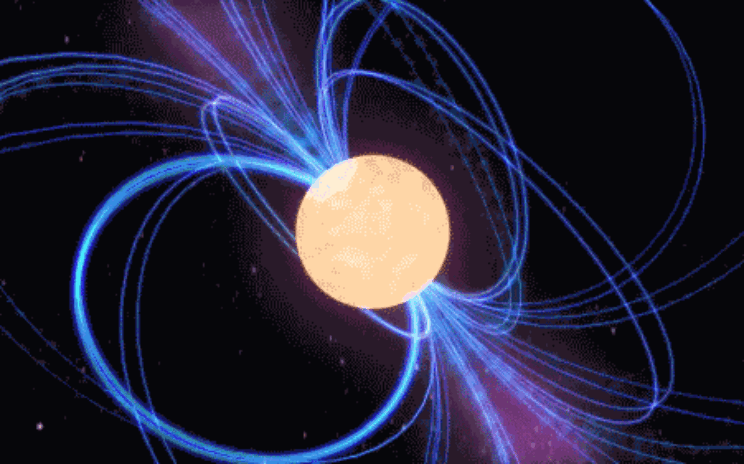
Reshared post from +annarita ruberto Pulsars, a kind of cosmic lighthouses The Pulsars (Pulsating Radio Sources) are rapidly rotating neutron stars with a very high magnetic field, which emit a collimated beam of radio waves.The radio emission, coming from the magnetic poles of the star, is confined within a small cone of emission and, if the magnetic axis is not aligned with the rotational one, the neutron star acts as a sort of cosmic lighthouse and an observer on Earth will see a sequence of pulses of radio waves. Let's see how a pulsar comes into being. When a massive star, exhausted its nuclear fuel, ends its life, it happens a supernova explosion and it remains a compact remnant . This object, named Neutron Star, has a radius of about 10 km and a mass equal about to 1.5 that one of the sun (whose radius is 700,000 miles). A Neutron Star is thus the "ash" that remains when a massive star collapses on itself and burns. The gravity force prevails on the electronic force that holds the atoms separated from each other and compresses them into a mass ten trillion times denser than a lead block. A single teaspoon […]
If I could I would want to see a neutron star before I die.. Originally shared by +annarita ruberto Pulsars, a kind of cosmic lighthouses The Pulsars (Pulsating Radio Sources) are rapidly rotating neutron stars with a very high magnetic field, which emit a collimated beam of radio waves.The radio emission, coming from the magnetic poles of the star, is confined within a small cone of emission and, if the magnetic axis is not aligned with the rotational one, the neutron star acts as a sort of cosmic lighthouse and an observer on Earth will see a sequence of pulses of radio waves. Let's see how a pulsar comes into being. When a massive star, exhausted its nuclear fuel, ends its life, it happens a supernova explosion and it remains a compact remnant . This object, named Neutron Star, has a radius of about 10 km and a mass equal about to 1.5 that one of the sun (whose radius is 700,000 miles). A Neutron Star is thus the "ash" that remains when a massive star collapses on itself and burns. The gravity force prevails on the electronic force that holds the atoms separated from each other and compresses them […]